
The CEHRT / Base EHR Gap
Posted on February 27, 2020
The practice has responsibilities under the MIPS program that 2015 Edition “CEHRT” has been implemented for the duration of the minimum-90-day MIPS Promoting Interoperability performance period. As will become clear below, there is some confusion regarding the defined term “CEHRT”. The practice should be clear on what it is attesting to and have the necessary documentation in place so that it can survive a possible MIPS pre-payment or post-payment audit; the practice should “trust but verify” that the HIT vendor is delivering on its obligations. After explaining the painful regulatory terminology, we provide a simple step-by-step procedure for how to verify and document that the practice does in fact have the required CEHRT.
“CEHRT” is a regulatory term defined by CMS; the current definition in the Federal Register reads as follows:
“Certified electronic health record technology (CEHRT) means the following: …
For 2019 and subsequent years, EHR technology (which could include multiple technologies) certified under the ONC Health IT Certification Program that meets the 2015 Edition Base EHR definition (as defined at 45 CFR 170.102) and has been certified to the 2015 Edition health IT certification criteria –
(i) At 45 CFR 170.315(a)(12) (family health history) and 45 CFR 170.315(e)(3) (patient health information capture); and
(ii) Necessary to be a Meaningful EHR User (as defined in this section), including the following:
(A) The applicable measure calculation certification criterion at 45 CFR 170.315(g)(1) or (2) for all certification criteria that support a meaningful use objective with a percentage-based measure.
(B) Clinical quality measure certification criteria that support the calculation and reporting of clinical quality measures at 45 CFR 170.315(c)(2) and (c)(3)(i) and (ii), and can be electronically accepted by CMS.”
42 CFR §495.4
“2015 Edition Base EHR” is in turn another regulatory term, but defined by ONC; the definition currently reads as follows in the Federal Register:
“2015 Edition Base EHR means an electronic record of health-related information on an individual that:
(1) Includes patient demographic and clinical health information, such as medical history and problem lists;
(2) Has the capacity:
(i) To provide clinical decision support;
(ii) To support physician order entry;
(iii) To capture and query information relevant to health care quality;
(iv) To exchange electronic health information with, and integrate such information from other sources; and
(3) Has been certified to the certification criteria adopted by the Secretary in § 170.315(a)(1), (2), or (3); (a)(5) through (9); (a)(11); (a)(15); (b)(1) and (6); (c)(1); (g)(7) through (9); and (h)(1) or (2)”
45 CFR §170.102
To summarize in more plain language, “CEHRT” requires additional mandatory certified capabilities beyond “2015 Edition Base EHR”, creating a “CEHRT / Base EHR Gap”
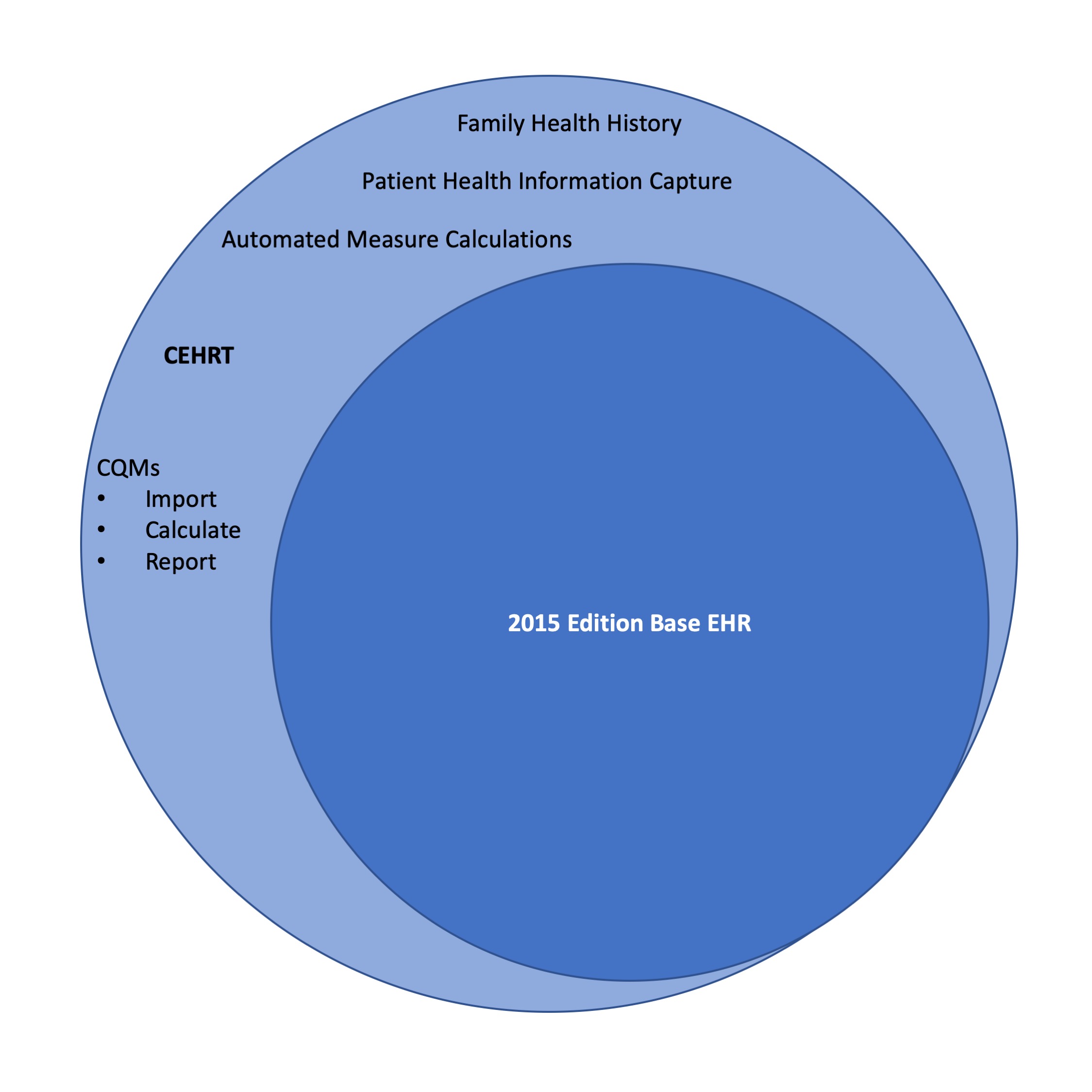
Figure 1 – the CEHRT / Base EHR Gap
The details of the CEHRT / Base EHR Gap are listed in Table 1 below (references to § 170 are for technical standards required for the ONC HIT Certification program):
| 45 CFR 170.315 | Description |
| (a)(12) | Family health history. Enable a user to record, change, and access a patient’s family health history in accordance with the familial concepts or expressions included in, at a minimum, the version of the standard in § 170.207(a)(4). |
| (c)(2) | Clinical quality measures—import and calculate
(i) Import. Enable a user to import a data file in accordance with the standard specified in § 170.205(h)(2) for one or multiple patients and use such data to perform the capability specified in paragraph (c)(2)(ii) of this section. A user must be able to execute this capability at any time the user chooses and without subsequent developer assistance to operate. (ii) Calculate each and every clinical quality measure for which it is presented for certification. |
| (c)(3)(i) and (ii) | Clinical quality measures—report. Enable a user to electronically create a data file for transmission of clinical quality measurement data:
(i) At a minimum, in accordance with the standards specified in § 170.205(h)(2) and § 170.205(k)(1) and (2). (ii) Optional. That can be electronically accepted by CMS.
HiQ note: (ii) may be optional in the ONC HIT Certification Program, but is mandatory for the CMS CEHRT definition for the MIPS program. |
| (e)(3) | Patient health information capture. Enable a user to:
(i) Identify, record, and access information directly and electronically shared by a patient (or authorized representative). (ii) Reference and link to patient health information documents. |
| (g)(1) | Automated numerator recording. For each EHR Incentive Programs percentage-based measure, technology must be able to create a report or file that enables a user to review the patients or actions that would make the patient or action eligible to be included in the measure’s numerator. The information in the report or file created must be of sufficient detail such that it enables a user to match those patients or actions to meet the measure’s denominator limitations when necessary to generate an accurate percentage.
HiQ note: (g)(1) or (g)(2) are required, not necessarily both. Also, the reference to “EHR Incentive Programs” should be interpreted as pertaining to the “Promoting Interoperability Programs” and in particular the MIPS Promoting Interoperability numeric measures. |
| (g)(2) | Automated measure calculation. For each EHR Incentive Programs percentage-based measure that is supported by a capability included in a technology, record the numerator and denominator and create a report including the numerator, denominator, and resulting percentage associated with each applicable measure.
HiQ note: (g)(1) or (g)(2) are required, not necessarily both. Also, the reference to “EHR Incentive Programs” should be interpreted as pertaining to the “Promoting Interoperability Programs” and in particular the MIPS Promoting Interoperability numeric measures. |
Table 1 – the CEHRT / Base EHR Gap
Unfortunately, neither the current CMS web page
nor the “fact sheet” linked to it (“2020 Promoting Interoperability Programs: 2015 Edition Certified Electronic Health Record Technology Fact Sheet”) detail the issue of the CEHRT / Base EHR gap; instead, CMS “punts” and refers to ONC:
“To learn which EHR systems and modules are certified for the Promoting Interoperability Programs, please visit the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL) on the ONC website.”
Visiting that ONC CHPL website provides the visitor a “CMS ID Creator” tool for creating a “CMS EHR Certification ID”. The problem is that this tool only verifies completeness relative to “2015 Edition Base EHR” and not “CEHRT”! The tool might say “Base Criteria: 100%” but with a disclaimer:
Such as, for example, requirements for the Quality Payment Program and its MIPS track!
Thus, the practice should use the CMS ID Creator tool, but then manually verify the gap requirements in Table 1. The practice shouldn’t simply take the HIT vendor’s verbal reassurances, but rather perform the following verification steps:
CEHRT Verification Procedure
- Find the product listing(s) for all the practice’s certified software as required for the MIPS program on the ONC CHPL website, possibly including multiple software applications, such as for example:
- EHR,
- eRx,
- Direct messaging,
- patient portal and
- QCDR – see below;
- Add the product(s) to the CMS ID Creator;
- Print the individual product’s CHPL description out for the practice’s MIPS audit file, showing all the certified capabilities and associated eCQMs;
- Verify that the CMS ID Creator shows 100%, and print this out for the MIPS audit file (including the CMS EHR Certification ID); and
- Verify that all items needed in Table 1 are accounted for; in particular verify that all eCQMs being reported by the practice are certified by the software.
It is worth pointing out that ONC removed the CQM certified capabilities (c)(2) and (c)(3) from its definition of Base EHR because it expected these to be provided by a registry rather than the EHR; ONC expects the Base EHR to implement certified capability (c)(1) “Clinical Quality Measures – capture and export”. This can be visualized as follows:

Figure 2 – EHR & QCDR Roles for CQMs
If the practice is using a QCDR for MIPS Quality reporting, that registry’s software may very well be certified for these mandatory CQM capabilities. In that case, the registry software should be added as a “product” in the above steps 1-5. For example, the FIGmd Registry Platform used by the great majority of professional society QCDR registries is in fact certified in this manner:
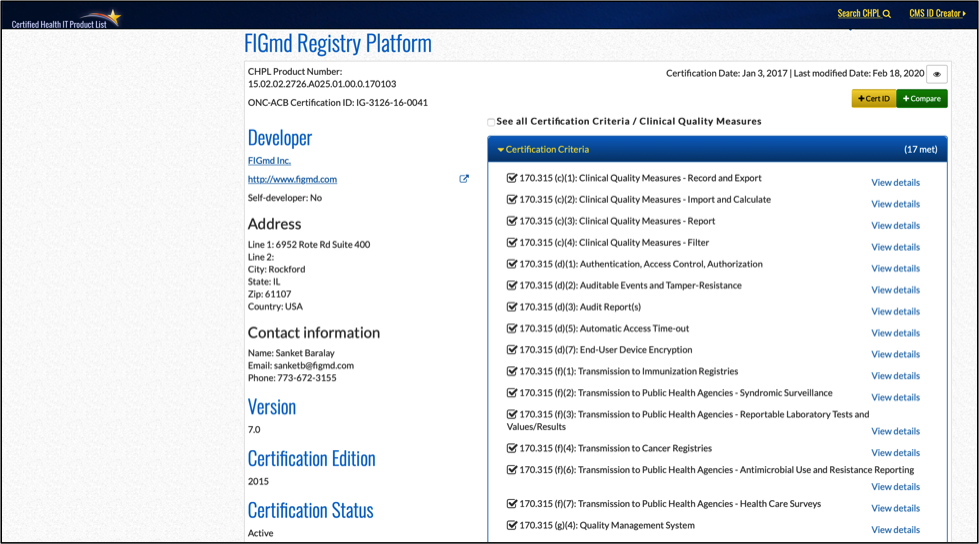
Figure 3 – FIGmd Registry Platform V7.0 Listing on the ONC CHPL Site
What if the practice finds that it is missing mandatory CEHRT capabilities? Hopefully this would be early enough in the MIPS performance year to take corrective action. The practice should first reach out to its EHR vendor to see if there is a solution, perhaps by implementing additional software products. If this is not possible in a timely manner but the practice qualifies as a small practice, it should consider to file for an EHR Hardship Exclusion (the deadline for such filing being Dec. 31, 2020 for the 2020 MIPS performance year). In other circumstances, it may be necessary for the practice to skip reporting MIPS Promoting Interoperability and forfeit the corresponding 25% of its MIPS Final Score; it is not recommended to intentionally falsify the practice’s CEHRT attestation, since this may result in greater penalties. In case of such negative situations, it may be necessary to begin searching for new CEHRT solutions from different vendors.
Recent Posts
- 2021 MIPS Final Rule – Practical Information and Strategic Issues December 7, 2020
- HiQ Adds Platinum Tier to MIPS EssentialsTM Service September 21, 2020
- 2021 MIPS Proposed Rule August 7, 2020
- Waiting for MVPs June 25, 2020
- Webinar – Interoperability and the Practice – June 24, July 8, & Aug 5,2020 May 11, 2020
